7.1: AsyncTask and AsyncTaskLoader
Contents:
- The UI thread
- AsyncTask
- AsyncTask usage
- Example of an AsyncTask
- Executing an AsyncTask
- Cancelling an AsyncTask
- Limitations of AsyncTask
- Loaders
- AsyncTaskLoader
- AsyncTaskLoader usage
- Related practical
- Learn more
There are two ways to do background processing in Android: using the AsyncTask class, or using the Loader framework, which includes an AsyncTaskLoader class that uses AsyncTask. In most situations you'll choose the Loader framework, but it's important to know how AsyncTask works so you can make a good choice.
In this chapter you'll learn why it's important to process some tasks in the background, off the UI thread. You'll learn how to use AsyncTask, when not to use AsyncTask, and the basics of using loaders.
The UI thread
When an Android app starts, it creates the main thread, which is often called the UI thread. The UI thread dispatches events to the appropriate user interface (UI) widgets, and it's where your app interacts with components from the Android UI toolkit (components from the android.widget and android.view packages).
Android's thread model has two rules:
1. Do not block the UI thread.
The UI thread needs to give its attention to drawing the UI and keeping the app responsive to user input. If everything happened on the UI thread, long operations such as network access or database queries could block the whole UI. From the user's perspective, the application would appear to hang. Even worse, if the UI thread were blocked for more than a few seconds (about 5 seconds currently) the user would be presented with the "application not responding" (ANR) dialog. The user might decide to quit your application and uninstall it.
To make sure your app doesn't block the UI thread:
- Complete all work in less than 16 ms for each UI screen.
- Don't run asynchronous tasks and other long-running tasks on the UI thread. Instead, implement tasks on a background thread using
AsyncTask(for short or interruptible tasks) orAsyncTaskLoader(for tasks that are high-priority, or tasks that need to report back to the user or UI).
2. Do UI work only on the UI thread.
Don't use a background thread to manipulate your UI, because the Android UI toolkit is not thread-safe.
AsyncTask
Use the AsyncTask class to implement an asynchronous, long-running task on a worker thread. (A worker thread is any thread which is not the main or UI thread.) AsyncTask allows you to perform background operations and publish results on the UI thread without manipulating threads or handlers.
When AsyncTask is executed, it goes through four steps:
onPreExecute()is invoked on the UI thread before the task is executed. This step is normally used to set up the task, for instance by showing a progress bar in the UI.doInBackground(Params...)is invoked on the background thread immediately afteronPreExecute()finishes. This step performs a background computation, returns a result, and passes the result toonPostExecute(). ThedoInBackground()method can also callpublishProgress(Progress...)to publish one or more units of progress.onProgressUpdate(Progress...)runs on the UI thread afterpublishProgress(Progress...)is invoked. UseonProgressUpdate()to report any form of progress to the UI thread while the background computation is executing. For instance, you can use it to pass the data to animate a progress bar or show logs in a text field.onPostExecute(Result)runs on the UI thread after the background computation has finished.
For complete details on these methods, see the AsyncTask reference. Below is a diagram of their calling order.
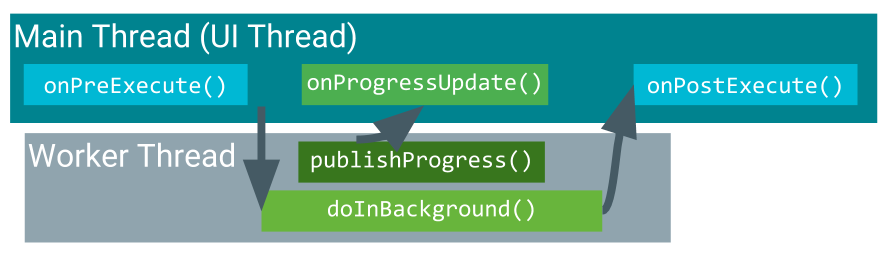
AsyncTask usage
To use the AsyncTask class, define a subclass of AsyncTask that overrides the doInBackground(Params...) method (and usually the onPostExecute(Result) method as well). This section describes the parameters and usage of AsyncTask, then shows a complete example.
AsyncTask parameters
In your subclass of AsyncTask, provide the data types for three kinds of parameters:
- "Params" specifies the type of parameters passed to
doInBackground()as an array. - "Progress" specifies the type of parameters passed to
publishProgress()on the background thread. These parameters are then passed to theonProgressUpdate()method on the main thread. - "Result" specifies the type of parameter that
doInBackground()returns. This parameter is automatically passed toonPostExecute()on the main thread.
Specify a data type for each of these parameter types, or use Void if the parameter type will not be used. For example:
public class MyAsyncTask extends AsyncTask <String, Void, Bitmap>{}
In this class declaration:
- The "Params" parameter type is
String, which means thatMyAsyncTasktakes one or more strings as parameters indoInBackground(), for example to use in a query. - The "Progress" parameter type is
Void, which means thatMyAsyncTaskwon't use thepublishProgress()oronProgressUpdate()methods. - The "Result" parameter type is
Bitmap.MyAsyncTaskreturns a Bitmap indoInbackground(), which is passed intoonPostExecute().
Example of an AsyncTask
private class DownloadFilesTask extends AsyncTask<URL, Integer, Long> {
protected Long doInBackground(URL... urls) {
int count = urls.length;
long totalSize = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
totalSize += Downloader.downloadFile(urls[i]);
publishProgress((int) ((i / (float) count) * 100));
// Escape early if cancel() is called
if (isCancelled()) break;
}
return totalSize;
}
protected void onProgressUpdate(Integer... progress) {
setProgressPercent(progress[0]);
}
protected void onPostExecute(Long result) {
showDialog("Downloaded " + result + " bytes");
}
}
The example above goes through three of the four basic AsyncTask steps:
doInBackground()downloads content, a long-running task. It computes the percentage of files downloaded from the index of theforloop and passes it topublishProgress(). The check forisCancelled()inside theforloop ensures that if the task has been cancelled, the system does not wait for the loop to complete.onProgressUpdate()updates the percent progress. It is is called every time thepublishProgress()method is called insidedoInBackground(), which updates the percent progress.doInBackground()computes the total number of bytes downloaded and returns it.onPostExecute()receives the returned result and passes it intoonPostExecute(), where it is displayed in a dialog.
The parameter types used in this example are:
URLfor the "Params" parameter type. TheURLtype means you can pass any number of URLs into the call, and the URLs are automatically passed into thedoInBackground()method as an array.Integerfor the "Progress" parameter type.Longfor the "Result" parameter type.
Executing an AsyncTask
After you define a subclass of AsyncTask, instantiate it on the UI thread. Then call execute() on the instance, passing in any number of parameters. (These parameters correspond to the "Params" parameter type discussed above).
For example, to execute the DownloadFilesTask task defined above, use the following line of code:
new DownloadFilesTask().execute(url1, url2, url3);
Cancelling an AsyncTask
You can cancel a task at any time, from any thread, by invoking the cancel() method.
- The
cancel()method returnsfalseif the task could not be cancelled, typically because it has already completed normally. Otherwise,cancel()returnstrue. - To find out whether a task has been cancelled, check the return value of
isCancelled()periodically fromdoInBackground(Object[]), for example from inside a loop as shown in the example above. TheisCancelled()method returnstrueif the task was cancelled before it completed normally. - After an
AsyncTasktask is cancelled,onPostExecute()will not be invoked afterdoInBackground()returns. Instead,onCancelled(Object)is invoked. The default implementation ofonCancelled(Object)simply invokesonCancelled()and ignores the result. - By default, in-process tasks are allowed to complete. To allow
cancel()to interrupt the thread that's executing the task, passtruefor the value ofmayInterruptIfRunning.
Limitations of AsyncTask
AsyncTask is impractical for some use cases:
Changes to device configuration cause problems.
When device configuration changes while an
AsyncTaskis running, for example if the user changes the screen orientation, the activity that created theAsyncTaskis destroyed and re-created. TheAsyncTaskis unable to access the newly created activity, and the results of theAsyncTaskaren't published.Old
AsyncTaskobjects stay around, and your app may run out of memory or crash.If the activity that created the
AsyncTaskis destroyed, theAsyncTaskis not destroyed along with it. For example, if your user exits the application after theAsyncTaskhas started, theAsyncTaskkeeps using resources unless you callcancel().
When to use AsyncTask:
- Short or interruptible tasks.
- Tasks that don't need to report back to UI or user.
- Low-priority tasks that can be left unfinished.
For all other situations, use AsyncTaskLoader, which is part of the Loader framework described next.
Loaders
Background tasks are commonly used to load data such as forecast reports or movie reviews. Loading data can be memory intensive, and you want the data to be available even if the device configuration changes. For these situations, use loaders, which are a set of classes that facilitate loading data into an activity.
Loaders use the LoaderManager class to manage one or more loaders. LoaderManager includes a set of callbacks for when the loader is created, when it's done loading data, and when it's reset.
Starting a loader
Use the LoaderManager class to manage one or more Loader instances within an activity or fragment. Use initLoader() to initialize a loader and make it active. Typically, you do this within the activity's onCreate() method. For example:
// Prepare the loader. Either reconnect with an existing one,
// or start a new one.
getLoaderManager().initLoader(0, null, this);
If you're using the Support Library, make this call using getSupportLoaderManager() instead of getLoaderManager(). For example:
getSupportLoaderManager().initLoader(0, null, this);
The initLoader() method takes three parameters:
- A unique ID that identifies the loader. This ID can be whatever you want.
- Optional arguments to supply to the loader at construction, in the form of a
Bundle. If a loader already exists, this parameter is ignored. - A
LoaderCallbacksimplementation, which theLoaderManagercalls to report loader events. In this example, the local class implements theLoaderManager.LoaderCallbacksinterface, so it passes a reference to itself,this.
The initLoader() call has two possible outcomes:
- If the loader specified by the ID already exists, the last loader created using that ID is reused.
- If the loader specified by the ID doesn't exist,
initLoader()triggers theonCreateLoader()method. This is where you implement the code to instantiate and return a new loader.Note: WhetherinitLoader()creates a new loader or reuses an existing one, the givenLoaderCallbacksimplementation is associated with the loader and is called when the loader's state changes. If the requested loader exists and has already generated data, then the system callsonLoadFinished()immediately (duringinitLoader()), so be prepared for this to happen.
Put the call toinitLoader()inonCreate()so that the activity can reconnect to the same loader when the configuration changes. That way, the loader doesn't lose the data it has already loaded.
Restarting a loader
When initLoader() reuses an existing loader, it doesn't replace the data that the loader contains, but sometimes you want it to. For example, when you use a user query to perform a search and the user enters a new query, you want to reload the data using the new search term. In this situation, use the restartLoader() method and pass in the ID of the loader you want to restart. This forces another data load with new input data.
About the restartLoader() method:
restartLoader()uses the same arguments asinitLoader().restartLoader()triggers theonCreateLoader()method, just asinitLoader()does when creating a new loader.- If a loader with the given ID exists,
restartLoader()restarts the identified loader and replaces its data. - If no loader with the given ID exists,
restartLoader()starts a new loader.
LoaderManager callbacks
The LoaderManager object automatically calls onStartLoading() when creating the loader. After that, the LoaderManager manages the state of the loader based on the state of the activity and data, for example by calling onLoadFinished() when the data has loaded.
To interact with the loader, use one of the LoaderManager callbacks in the activity where the data is needed:
- Call
onCreateLoader()to instantiate and return a new loader for the given ID. - Call
onLoadFinished()when a previously created loader has finished loading. This is typically the point at which you move the data into activity views. - Call
onLoaderReset()when a previously created loader is being reset, which makes its data unavailable. At this point your app should remove any references it has to the loader's data.
The subclass of the Loader is responsible for actually loading the data. Which Loader subclass you use depends on the type of data you are loading, but one of the most straightforward is AsyncTaskLoader, described next. AsyncTaskLoader uses an AsyncTask to perform tasks on a worker thread.
AsyncTaskLoader
AsyncTaskLoader is the loader equivalent of AsyncTask. AsyncTaskLoader provides a method, loadInBackground(), that runs on a separate thread. The results of loadInBackground() are automatically delivered to the UI thread, by way of the onLoadFinished() LoaderManager callback.
AsyncTaskLoader usage
To define a subclass of AsyncTaskLoader, create a class that extends AsyncTaskLoader<D>, where D is the data type of the data you are loading. For example, the following AsyncTaskLoader loads a list of strings:
public static class StringListLoader extends AsyncTaskLoader<List<String>> {}
Next, implement a constructor that matches the superclass implementation:
- Your constructor takes the application context as an argument and passes it into a call to
super(). - If your loader needs additional information to perform the load, your constructor can take additional arguments. In the example shown below, the constructor takes a query term.
public StringListLoader(Context context, String queryString) {
super(context);
mQueryString = queryString;
}
To perform the load, use the loadInBackground() override method, the corollary to the doInBackground() method of AsyncTask. For example:
@Override
public List<String> loadInBackground() {
List<String> data = new ArrayList<String>;
//TODO: Load the data from the network or from a database
return data;
}
Implementing the callbacks
Use the constructor in the onCreateLoader() LoaderManager callback, which is where the new loader is created. For example, this onCreateLoader() callback uses the StringListLoader constructor defined above:
@Override
public Loader<List<String>> onCreateLoader(int id, Bundle args) {
return new StringListLoader(this, args.getString("queryString"));
}
The results of loadInBackground() are automatically passed into the onLoadFinished() callback, which is where you can display the results in the UI. For example:
public void onLoadFinished(Loader<List<String>> loader, List<String> data) {
mAdapter.setData(data);
}
The onLoaderReset() callback is only called when the loader is being destroyed, so you can leave onLoaderReset() blank most of the time, because you won't try to access the data after the loader is destroyed.
When you use AsyncTaskLoader, your data survives device-configuration changes. If your activity is permanently destroyed, the loader is destroyed with it, with no lingering tasks that consume system resources.
Loaders have other benefits too, for example they let you monitor data sources for changes and reload the data if a change occurs. You learn more about the specifics of loaders in a future lesson.
Related practical
The related exercises and practical documentation is in Android Developer Fundamentals: Practicals.
